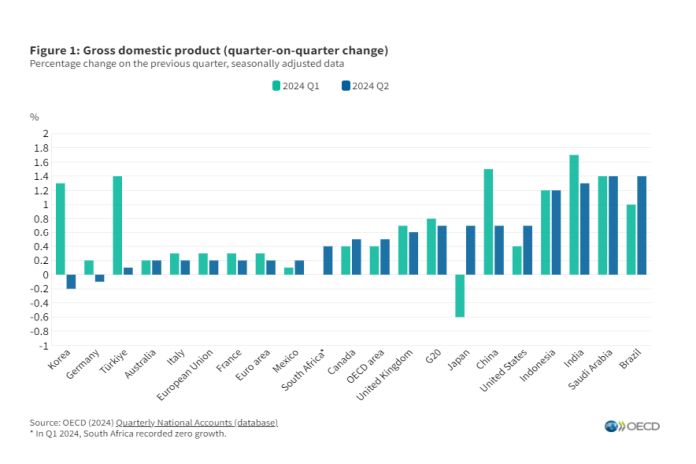
PARIS, France – Gross domestic product (GDP) growth in the G20 area remained relatively stable in Q2 2024, with a 0.7 percent quarter-on-quarter increase according to provisional estimates, slightly down from 0.8 percent in the previous quarter (Figure 1).
China, India, and the United States contributed the most to G20’s economic growth in Q2 2024,1 although Brazil and Saudi Arabia saw the highest growth rates (both at 1.4%). Growth in both China and India slowed (from 1.5% to 0.7% and from 1.7% to 1.3%, respectively). Japan saw a significant recovery, from a 0.6 percent contraction in Q1 to a 0.7 percent expansion in Q2, whereas the United States recorded a more modest increase, from 0.4 percent to 0.7 percent.
The remaining G20 countries experienced weaker growth than the G20 as a whole, with GDP in Korea and Germany even contracting (by 0.2% and 0.1%, respectively). Growth in Türkiye slowed sharply, from 1.4 percent to 0.1 percent. France, Italy, and the United Kingdom recorded minor decreases (with growth rates of 0.2%, 0.2% and 0.6% respectively).
On the other hand, Canada and Mexico saw small increases (to 0.5% and 0.2%, respectively), while growth picked up in South Africa to 0.4 percent in Q2, after no growth in Q1. Growth remained stable in Australia at 0.2 percent and little change was observed in the European Union and the euro area, both zones recording 0.2 percent in Q2 compared to 0.3 percent in Q1 2024.
Compared with the same quarter of the previous year, GDP in the G20 area grew by 3.1 percent in Q2 2024, slightly down from 3.2 percent in the previous quarter (Table 2). Among G20 economies, India recorded the highest year-on-year growth rate (6.8%) in Q2, followed by Indonesia (5.0%). Japan recorded the largest fall (-0.9%).