- Rapid growth of this opaque and highly interconnected segment of the financial system could heighten financial vulnerabilities given its limited oversight
By Charles Cohen, Caio Ferreira, Fabio Natalucci, Nobuyasu Sugimoto
The private credit market, in which specialized non-bank financial institutions such as investment funds lend to corporate borrowers, topped $2.1 trillion globally last year in assets and committed capital. About three-quarters of this was in the United States, where its market share is nearing that of syndicated loans and high-yield bonds.
This market emerged about three decades ago as a financing source for companies too large or risky for commercial banks and too small to raise debt in public markets. In the past few years, it has grown rapidly as features such as speed, flexibility, and attentiveness have proved valuable to borrowers. Institutional investors such as pension funds and insurance companies have eagerly invested in funds that, though illiquid, offered higher returns and less volatility.
Private corporate credit has created significant economic benefits by providing long-term financing to corporate borrowers. However, the migration of this lending from regulated banks and more transparent public markets to the more opaque world of private credit creates potential risks. Valuation is infrequent, credit quality isn’t always clear or easy to assess, and it’s hard to understand how systemic risks may be building given the less-than-clear interconnections between private credit funds, private equity firms, commercial banks, and investors.
Today, immediate financial stability risks from private credit appear to be limited. However, given that this ecosystem is opaque and highly interconnected, and if fast growth continues with limited oversight, existing vulnerabilities could become a systemic risk for the broader financial system.
We identify a number of fragilities in our April 2024 Global Financial Stability Report.
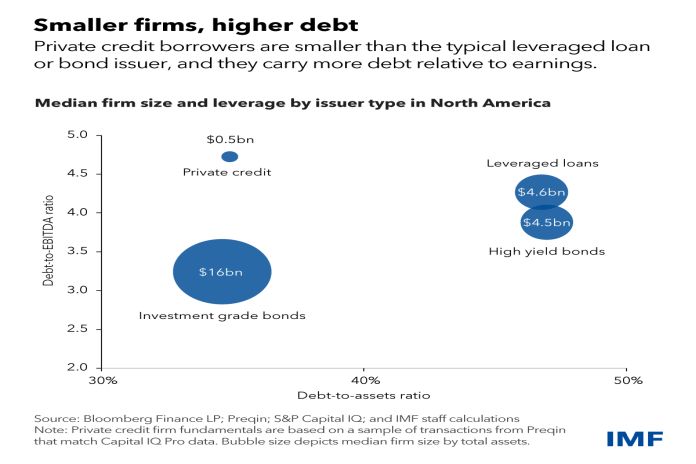
First, companies that tap the private credit market tend to be smaller and carry more debt than their counterparts with leveraged loans or public bonds. This makes them more vulnerable to rising rates and economic downturns. With the recent rise in benchmark interest rates, our analysis indicates that more than one-third of borrowers now have interest costs exceeding their current earnings.
The rapid growth of private credit has recently spurred increased competition from banks on large transactions. This, in turn has put pressure on private credit providers to deploy capital, leading to weaker underwriting standards and looser loan covenants, some signs of which have already been noted by supervisory authorities.
Second, private market loans rarely trade, and therefore can’t be valued using market prices. Instead, they are often marked only quarterly using risk models, and may suffer from stale and subjective valuations across funds. Our analysis comparing private credit to leveraged loans (which trade regularly in a more liquid and transparent market) shows that, despite having lower credit quality, private credit assets tend to have smaller markdowns during times of stress.
Third, while private credit fund leverage appears to be low, the potential for multiple layers of hidden leverage within the private credit ecosystem does raise concerns given the lack of data. Leverage is deployed also by investors in these funds and by the borrowers themselves. This layering of leverage makes it difficult to assess potential systemic vulnerabilities of this market.
Fourth, there appears to be a significant degree of interconnectedness in the private credit ecosystem. While banks do not seem to have a material exposure to private credit in aggregate, the Federal Reserve has estimated that US private credit borrowing amounted to less than about $200 billion, less than 1 percent of US bank assets, some banks may have concentrated exposures to the sector. In addition, a select group of pension funds and insurers are diving deeper into private credit waters, significantly upping their share of these less-liquid assets. This includes private-equity-influenced life insurance companies, as we discussed in a recent report.
Finally, though liquidity risks appear limited today, a growing retail presence may alter this assessment. Private credit funds use long-term capital lockups and impose constraints on investor redemptions to align the investment horizon with the underlying illiquid assets. But new funds targeted at individual investors may have higher redemption risks. Although these risks are mitigated by liquidity management tools (such as gates and fixed redemption periods), they have not been tested in a severe runoff scenario.
Overall, although these vulnerabilities currently they do not pose a systemic risk to the broader financial sector, they may continue to build, with implications for the economy. In a severe downturn, credit quality could deteriorate sharply, spurring defaults and significant losses. Opacity could make these losses hard to assess. Banks could curb lending to private credit funds, retail funds could face large redemptions, and private credit funds and their institutional investors could experience liquidity strains. Significant interconnectedness could affect public markets, as insurance companies and pension funds may be forced to sell more liquid assets.
The cumulative effect of these links may have significant economic implications should stress in private credit markets result in a pullback from lending to companies. Severe data gaps make monitoring these vulnerabilities across financial markets and institutions more difficult and may delay proper risk assessment by policymakers and investors.
Policy implications
It is imperative to adopt a more vigilant regulatory and supervisory posture to monitor and assess risks in this market.
- Authorities should consider a more active supervisory and regulatory approach to private credit, focusing on monitoring and risk management, leverage, interconnectedness, and concentration of exposures.
- Authorities should enhance cooperation across industries and national borders to address data gaps and make risk assessments more consistent across financial sectors.
- Regulators should improve reporting standards and data collection to better monitor private credit’s growth and its implications for financial stability.
- Securities regulators should pay close attention to liquidity and conduct risk in private credit funds, especially retail, that may face higher redemption risks. Regulators should implement recommendations on product design and liquidity management from the Financial Stability Board and the International Organization of Securities Commissions.
*** This blog is based on Chapter 2 of the April 2024 Global Financial Stability Report: “The Rise and Risks of Private Credit.”